Boost Efficiency: TOON vs JSON Prompting Guide
Maximizing Efficiency with TOON: A Comprehensive Guide to Prompting Over JSON
Prompting with TOON (Token-Oriented Object Notation) is a compact alternative to JSON for LLM prompts. It reduces structural overhead, which can lower token usage, extend usable context, and improve parsing consistency when paired with a clear schema.
This guide outlines the TOON data structure, compares token impact versus JSON, shows implementation patterns, and provides a simple way to benchmark on your own data. It applies to agents, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines, and tool-calling workflows.
Understanding TOON: An Introduction

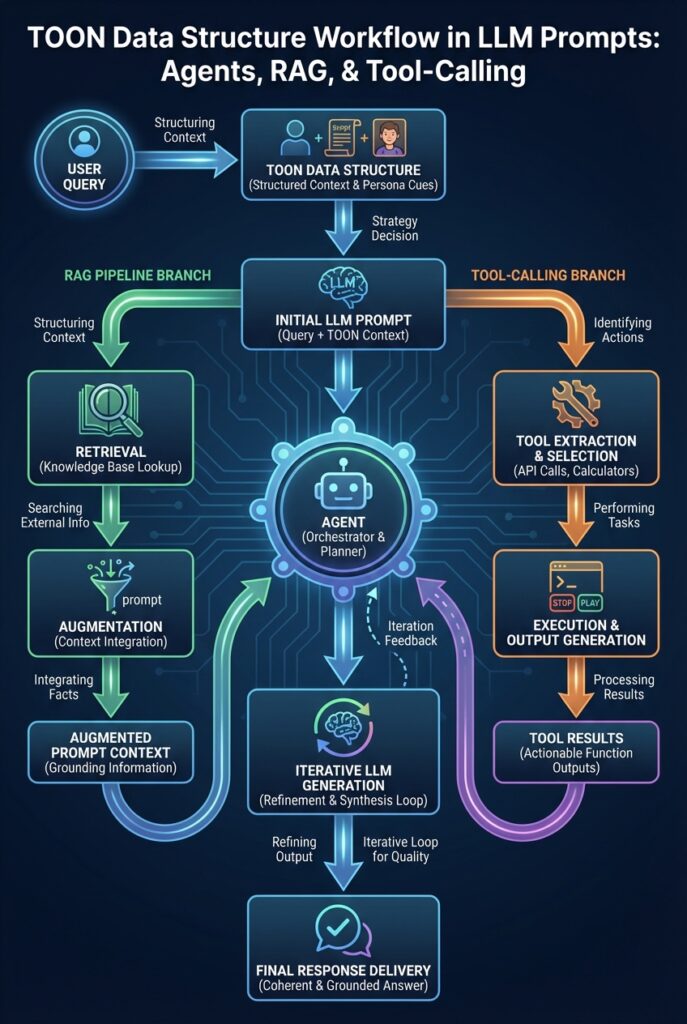
What is TOON?
TOON (Token-Oriented Object Notation) is a compact, human-readable, and model-friendly representation for structured data. It is designed to minimize token overhead while preserving semantics. Instead of heavy punctuation, repeated quotes, and verbose keys, TOON favors short aliases and minimal delimiters to reduce tokens in prompts and responses.
TOON is a prompt-first format intended for readability by both humans and models. It is not a general-purpose replacement for JSON in interfaces that require strict interoperability and mature tooling; it is most effective inside LLM-centric workflows.
Example comparison (conceptual):
JSON:
{
"user": { "name": "Ana", "age": 29, "interests": ["music", "ai"] },
"task": "recommend articles",
"limit": 5
}TOON (schema-alias + compact delimiters):
# schema aliases
# u: user, n: name, g: age, i: interests, t: task, l: limit
u(n=Ana|g=29|i=[music,ai]); t=recommend_articles; l=5In prompting with TOON, short aliases and lightweight separators can reduce tokens while staying readable. This is especially helpful for repeated structures like chat messages or tool-call arguments.
Why Consider TOON Over JSON?
JSON is ubiquitous, well-supported, and well-suited to APIs and storage. For LLM prompts, however, quotes around every key, verbose keys repeated across objects, and whitespace can inflate token counts. TOON reduces predictable overhead while keeping enough structure for reliable parsing. As a result, prompting with TOON can:
- Reduce token usage (the exact savings depend on schema and content; benchmark on your data).
- Increase the amount of content you can fit in a given context window.
- Improve clarity for models when accompanied by a simple schema.
- Enable consistent, compact tool-call and function-argument representations.
For LLM-centric pipelines (e.g., agents, RAG, tool use), TOON vs JSON can deliver material gains in cost and context usage. The impact varies by workload, so measure in your stack.
Advantages of Using TOON
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Every token counts. If your application processes many requests, even small per-prompt reductions compound. TOON choices—short aliases, minimal punctuation, and consistent delimiters—reduce LLM token usage without sacrificing structure.
Practical advantages of prompting with TOON:
- Lower API bills: Fewer prompt tokens and fewer completion tokens when the assistant mirrors TOON output.
- Lower latency: Smaller inputs can reduce input processing time. While model speed depends on many factors, token count is a primary driver.
- Fewer formatting errors: Clear, repeatable patterns tend to reduce formatting mistakes compared to verbose JSON in long chains.
Example (chat message list):
JSON messages:
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Suggest 3 travel ideas for Japan."}
]TOON messages:
m:sys|You are a helpful assistant.
m:usr|Suggest 3 travel ideas for Japan.Prompting with TOON trims repeated keys and quotes, directly cutting tokens.
Increased Context Window
By compressing structure, prompting with TOON lets you fit more examples, longer context, or richer tool metadata within the same context window. This can improve few-shot performance, retrieval coverage, and tool selection accuracy.
- More demonstrations: Pack more examples for program synthesis or structured generation tasks.
- Extended transcripts: Keep longer conversation history to preserve nuance.
- Richer metadata: Include more RAG snippets, citations, or constraints within limits.
TOON format benefits compound in multi-turn or multi-tool scenarios, where JSON’s overhead accumulates.
Challenges and Limitations of TOON
Tooling Maturity of TOON
JSON wins on tooling. It has validators, serializers, diff tools, and IDE support everywhere. TOON is newer and less standardized. While it is simple to parse, you may need to implement or adopt lightweight libraries to validate, serialize, and lint. Until TOON has broad, formal specs and parsers, you will balance performance gains against tooling gaps.
Mitigation tips when prompting with TOON:
- Keep a stable schema with comments and examples in your repo.
- Build a small parser/serializer and ship tests alongside it.
- Fallback to JSON for interfaces that demand strict interoperability.
Training Models for TOON
Most base models follow consistent patterns with brief instruction. To get predictable outputs when prompting with TOON:
- Document the grammar in the system prompt: Provide one or two short examples.
- Use few-shot demonstrations: Show how inputs and outputs map to the TOON structure.
- Constrain outputs: Ask for “TOON only” responses and add format checks on your side.
- Consider fine-tuning: If TOON is central to your stack, fine-tuning can further stabilise adherence.
For safety, validate TOON output server-side and handle exceptions gracefully.
Implementing TOON in Current Workflows
Benchmarking TOON vs JSON
To justify adoption, benchmark token counts and latency. Here is a simple Python script using tiktoken to compare JSON vs TOON on your own payloads:
# pip install tiktoken
import tiktoken
enc = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base") # adjust for your model
def tokens(x: str) -> int:
return len(enc.encode(x))
json_payload = '{"user": {"name": "Ana", "age": 29, "interests": ["music", "ai"]}, "task": "recommend articles", "limit": 5}'
toon_payload = 'u(n=Ana|g=29|i=[music,ai]); t=recommend_articles; l=5'
print("JSON tokens:", tokens(json_payload))
print("TOON tokens:", tokens(toon_payload))
print("Savings:", round((1 - tokens(toon_payload)/tokens(json_payload)) * 100, 1), "%")Benchmark across your real prompts: multi-turn logs, tool calls, and RAG inputs. In many pipelines, prompting with TOON yields measurable savings; verify with your own data.
Conversion Strategies
Migration does not have to be all-or-nothing. Convert targeted parts where JSON overhead is highest. Effective strategies for prompting with TOON:
- Alias Maps: Maintain a schema that maps verbose keys to 1–2 letter aliases.
- Minimal Delimiters: Prefer key=value pairs with | separators inside objects and ; between objects.
- Type Hints When Needed: Use lightweight prefixes (n: for number, b: for boolean) only when ambiguity matters.
- Arrays Without Quotes: For simple tokens (no spaces), drop quotes inside arrays to reduce overhead.
- Selective JSON: Keep JSON for cross-system interfaces; use TOON internally for model-facing prompts.
Example: A tiny Python helper to convert a constrained JSON structure to TOON using a schema map.
from typing import Any, Dict, List
ALIAS = {
"user": "u",
"name": "n",
"age": "g",
"interests": "i",
"task": "t",
"limit": "l",
}
SEPARATOR_INNER = "|"
SEPARATOR_OUTER = "; "
def to_toon(value: Any) -> str:
if isinstance(value, dict):
parts = []
for k, v in value.items():
a = ALIAS.get(k, k)
parts.append(f"{a}={to_toon(v)}")
return "(" + SEPARATOR_INNER.join(parts) + ")"
elif isinstance(value, list):
return "[" + ",".join(to_toon(v) for v in value) + "]"
elif isinstance(value, str):
# Quote only if spaces or punctuation that might confuse parsing
return value if value.replace(" ", "").isalnum() else '"' + value.replace('"', '\\"') + '"'
else:
return str(value)
def json_to_toon(payload: Dict[str, Any]) -> str:
segments = []
for k, v in payload.items():
a = ALIAS.get(k, k)
if isinstance(v, dict):
segments.append(f"{a}{to_toon(v)}")
else:
segments.append(f"{a}={to_toon(v)}")
return SEPARATOR_OUTER.join(segments)
# Example usage
payload = {
"user": {"name": "Ana", "age": 29, "interests": ["music", "ai"]},
"task": "recommend articles",
"limit": 5
}
print(json_to_toon(payload))
# u(n=Ana|g=29|i=[music,ai]); t=recommend_articles; l=5And a minimal parser to convert TOON back to JSON (for controlled schemas):
import re
REV = {v: k for k, v in ALIAS.items()}
# NOTE: This simplistic parser assumes no nested parentheses beyond one level,
# arrays are flat, and values are alnum or quoted. Extend for your needs.
def parse_value(s: str):
s = s.strip()
if s.startswith('"') and s.endswith('"'):
return s[1:-1].replace('\\"', '"')
if s.startswith('[') and s.endswith(']'):
inner = s[1:-1]
if not inner.strip():
return []
items = [parse_value(p) for p in inner.split(',')]
return items
if s.startswith('(') and s.endswith(')'):
inner = s[1:-1]
obj = {}
for pair in inner.split('|'):
k, v = pair.split('=', 1)
key = REV.get(k, k)
obj[key] = parse_value(v)
return obj
# try int
if re.fullmatch(r"-?\d+", s):
return int(s)
# try float
if re.fullmatch(r"-?\d+\.\d+", s):
return float(s)
return s
def toon_to_json(s: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
obj = {}
for seg in [p.strip() for p in s.split(';') if p.strip()]:
if '(' in seg and seg.endswith(')'):
a = seg.split('(', 1)[0]
body = '(' + seg.split('(', 1)[1]
key = REV.get(a, a)
obj[key] = parse_value(body)
else:
a, v = seg.split('=', 1)
key = REV.get(a.strip(), a.strip())
obj[key] = parse_value(v)
return obj
# Example
s = 'u(n=Ana|g=29|i=[music,ai]); t=recommend_articles; l=5'
print(toon_to_json(s))These helpers enable hybrid pipelines where prompting with TOON is used internally while external interfaces remain JSON-based.
Applications and Use Cases for TOON
TOON shines wherever structured text meets LLMs. The following scenarios often benefit from prompting with TOON:
- Agent Tool Calls: Represent function arguments, results, and tool metadata succinctly.
- RAG Pipelines: Encode retrieved snippets, citations, and doc IDs compactly.
- Long Conversations: Store message roles and content in an ultra-compact chat log format.
- Evaluation Harnesses: Fit more test cases and assertions into a single evaluation pass.
- Edge and Mobile: Conserve bandwidth and latency where token budgets are tight.
TOON in AI Models
Here’s a practical pattern for prompting with TOON in chat tasks. Provide a short grammar and two exemplars in the system message, then enforce output:
System (excerpt):
You will read and write data in TOON (Token-Oriented Object Notation).
Grammar:
- Objects: alias(key=value|key=value)
- Top-level segments separated by '; '
- Arrays: [v1,v2,...]; Use quotes only if spaces or punctuation
Aliases:
- m: message; r: role; c: content; t: tool; a: args; o: output
Examples:
m(r=sys|c=You are a helpful assistant.);
m(r=usr|c=Suggest 3 travel ideas for Japan.);
When invoking a tool:
m(r=asst|t=search|a(topic=Japan|limit=3));
Tool returns:
m(r=tool|o=["Tokyo itinerary","Kyoto food tour","Hokkaido hiking"]);User prompt using TOON messages:
m(r=usr|c=Plan a 2-day Kyoto trip with a budget focus. Include neighborhoods.)Assistant must reply in TOON:
m(r=asst|c=Day1: Higashiyama/Philosopher's Path...
Advantages of Using TOON over JSON
Advantage
TOON Benefit
Impact on Efficiency
Reduced Parsing Complexity
Streamlined format reduces errors
Speeds up data processing times
Enhanced Data Compression
More compact serialization
Saves storage and bandwidth
Better Human Readability
More intuitive structure
Facilitates easier debugging
Higher Interoperability
Supports more data types
Improves integration with different systems
Faster Parsing Speed
Optimized for rapid parsing
Reduces application load time
|t=search|a(topic=Kyoto hostels|limit=3))This pattern guides the model to remain structured and compact, keeping prompting with TOON consistent across turns.
Future of TOON Development
Tooling and Support Enhancements
TOON is evolving. Potential focus areas aim to make prompting with TOON easier and safer:
- Formal Spec and Schemas: Publish a concise grammar plus a schema notation for alias maps, types, and constraints.
- Parsers and Linters: Libraries for popular languages (Python, JS/TS, Go) with strict and permissive modes.
- Editor Plugins: Syntax highlighting and validation in VS Code and JetBrains IDEs.
- Converters: Seamless TOON ↔ JSON transforms, including streaming and partial updates.
- Validation Hooks: Schema-level checks to catch malformed outputs before downstream consumption.
- Bench Suites: Automated token, latency, and accuracy benchmarks across models for TOON vs JSON.
If adoption grows, a small ecosystem of tools may emerge, making prompting with TOON straightforward for complex agent systems and high-throughput workloads.
Technical Notes and Best Practices
- Design for Your Model: Different tokenizers behave differently. Validate that your chosen delimiters are token-efficient for your target model.
- Schema Discipline: Centralise alias maps and keep them stable to avoid brittle parsing.
- Error Handling: Always validate model outputs. On failure, ask the model to reformat or fall back to JSON for that turn.
- Security: Treat TOON like any input—sanitise user-provided values and guard tool-call boundaries.
- Document Examples: Few-shot examples are a fast way to stabilise prompting with TOON in production.
Extended Example: Tool Invocation
JSON tool call:
{
"tool": "search_hotels",
"args": {"city": "Kyoto", "max_price": 120, "n": 3}
}TOON equivalent:
t=search_hotels; a(city=Kyoto|max_price=120|n=3)Server-side routing pseudocode (JavaScript):
function routeTool(toon) {
// very naive extraction; use a real parser in production
const segs = toon.split(';').map(s => s.trim()).filter(Boolean);
const map = Object.fromEntries(segs.map(s => {
const [k, rest] = s.split('=');
return [k.trim(), rest.trim()];
}));
if (map.t === 'search_hotels') {
const args = map.a.slice(1, -1) // remove parentheses
.split('|')
.reduce((acc, kv) => { const [k, v] = kv.split('='); acc[k] = v; return acc; }, {});
return searchHotels(args.city, Number(args.max_price), Number(args.n));
}
}This pattern keeps your external API JSON-based while making internal prompting with TOON lean and predictable.
FAQ
Is TOON a standard? Not yet. It is a pragmatic approach to reduce overhead in prompts. You can adopt a house style while the ecosystem matures.
How much can I save? Savings depend on content and schema. Some workloads show substantial reductions; benchmark your own data to quantify impact.
Will models understand TOON? Most modern models follow simple grammars with minimal instruction and examples. For mission-critical outputs, add validation and retries. Fine-tuning can further improve adherence.
Can I mix TOON and JSON? Yes. Many teams keep JSON for public APIs and storage, and use TOON internally for model-facing prompts. Hybrid prompting with TOON is common.
What about complex nested data? TOON supports nesting, but keep it simple. If structures become too complex, fall back to JSON for that section.
Prompting with TOON focuses tokens on meaning rather than markup. By adopting a compact, model-aligned representation, you can scale interactions, reduce costs, and improve reliability where it matters most—inside the prompt. Start with targeted conversions, benchmark your workloads, and expand where the gains are clear.
